| Case Name |
Runaway reaction during manufacturing pesticide due to a decomposition reaction of tarry waste. |
| Pictograph |
|
| Date |
May 10, 1973 |
| Place |
Oita, Oita, Japan |
| Location |
Pesticide factory |
| Overview |
In 1973, tarry waste from a pesticide manufacturing plant started a decomposition reaction due to a temperature rise at a chemical plant in Oita prefecture. The resulting malodorous decomposition gases leaked from the manhole flange of the seal drum. Residents downwind were evacuated, but 42 were injured (acute pharyngitis). |
| Incident |
The temperature of tarry waste increased due to a utility condition change during temporary storage of tarry waste on manufacturing pesticide. Toxic gas caused by a decomposition reaction leaked. |
| Processing |
Waste and disposal |
| Process Flow |
Fig2.Unit process flow
|
|
Fig3.Unit process flow
|
| Chemical Reaction |
Other |
| Chemical Equation |
Fig4.Chemical reaction formula 1
|
| Substance |
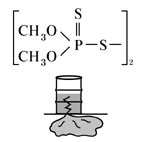
O,O'-dimethyl phosphorodithioate sodium salt, Fig5 |
| O,O'-dimethyl phosphorodithioate dimer, Fig6 |
| Type of Accident |
Leakage, health hazard |
| Sequence |
At a pesticide plant, sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide were added to waste water containing O,O'- dimethyl phosphorodithioate sodium salt. The resultant dimethyl phosporodithioate dimer was separated and stored temporarily in a drum. At the temporary storage drum, the dimer was hydrolyzed severely and produced toxic gases such as hydrogen sulfide, methanol, carbon disulfide, methyl mercaptan, dimethyl dithioether, and dimethyl disulfide. The gases spouted from the flange of a manhole of a seal-drum of the temporary storage and gave off a stench. |
| Cause |
The temporary storage drum was equipped with a cooling water jacket and an agitator. To maintain the temperature of tarry waste at 60°C, 70°C warm water was circulated through the jacket. The warm water was supplied with a mixture of industrial water and steam. As the industrial water was also used at another location, the temperature of the jacket water rose to 90°C, and the inner wall of the drum also reached 90°C because the contents of the drum did not reach the level of the cooling water jacket. When tarry waste touched the 90°C inner wall on being agitated, a decomposition reaction started. Decomposition gradually proceeded, and resulted in a runaway reaction. A small volume of water was also introduced to the drum to confirm completion of tarry material transfer. The water generated a hydrolytic reaction and promoted the decomposition reaction. |
| Knowledge Comment |
1. When a significant amount of chemicals is handled, the specific hazards of the chemicals should be understood through preliminary experiments.
2. The properties of waste should be grasped even if it is to be incinerated.
3. Care should be taken in changes of utility as well as process fluid. |
| Background |
1. A temperature rise of warm water resulted in tarry waste overheating. Warm water and water for field work were taken out from the same industrial water piping. As the water for field work began to be used, the warm water temperature began to rise as the water supply decreased. It is an obvious mistake in the process design. The operation side did not recognize the defect in the piping.
2. Basically, there was no recognition that heating of tarry waste at this temperature results in decomposition, which was confirmed by an experiment after the accident. There seemed to have been a lack of knowledge on the waste disposal process. |
| Reason for Adding to DB |
Example of insufficient analysis of reaction hazards of waste at an in-house development process |
| Scenario |
| Primary Scenario
|
Insufficient Analysis or Research, Insufficient Prior Research, Oversight of Reaction Danger, Poor Value Perception, Poor Safety Awareness, Inadequate Risk Recognition, Planning and Design, Poor Planning, Much Influences from Other Usage, Regular Movement, Careless Movement, Insufficient Flow Rate, Bad Event, Chemical Phenomenon, Hydrolysis, Secondary Damage, External Damage, Leakage, Bodily Harm, Sickness, 42 person nearby sickness
|
|
| Sources |
Tetsuzo Kitagawa. Explosion caused by the decomposition of the tarry waste. Analysis of explosion hazard. pp.256-260(1980)
High Pressure Gas Safety Inst. of Japan. Accident Examples in Complexes. pp.219-220(1991)
Masamitsu Tamure. Masahide Wakakura. Explosion of tarry waste. Reaction danger - Accident case and analysis - p175(1995)
|
| Number of Injuries |
42 |
| Multimedia Files |
Fig5.Chemical formula
|
|
Fig6.Chemical formula
|
| Field |
Chemicals and Plants
|
| Author |
YOSHINAGA, Jun (Graduate School of New Frontier Sciences, The University of Tokyo)
TAMURA, Masamitsu (Center for Risk Management and Safety Sciences, Yokohama National University)
|
|