| Case Name |
Explosion and fire at an outdoor tank to start storage before completion of attached facilities |
| Pictograph |
|
| Date |
July 10, 1989 |
| Place |
Wakayama, Wakayama, Japan |
| Location |
Oil terminal |
| Overview |
The ethyl acrylate storage tank was filled with a combustible gas-air mixture generated by vaporized ethyl acrylate up to the deodorization piping. It was ignited by welding sparks. Although a refrigerator was being installed, the accident occurred before the completion of it due to inadequate management of the stored solvent. In hot work on the piping directly connected to the tank, basic safety management such as separation from the tank or replacement with inert gas was totally neglected. |
| Incident |
The solvents were stored in a tank though a refrigerator at attached facilities had not been completed. The organic solvents in the tank evaporated, leaked, and ignited. |
| Processing |
Storage |
| Process Flow |
Fig2.Schematic drawings of facilities
|
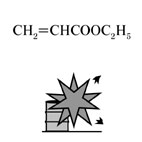
| Substance |
Ethyl acrylate, Fig3 |
| Type of Accident |
Leakage, explosion, fire |
| Sequence |
1. Installation of a cooling unit only for an ethyl acrylate tank and piping work for a deodorizer were carried out.
2. Ethyl acrylate was received and put in the tank before completion of the cooling unit.
3. Work on deodorization piping was carried out twenty days later.
4. The tank exploded suddenly and burned. Ethyl acrylate burned for 12 hours.
5. The valve in the piping connecting the tank and the deodorization tower was opened or leaked, and a blind plate was not inserted. |
| Cause |
1. Although the solvent should have been received after completion of the cooling system, it was received before completion. As a result, the solvent evaporated due to outside temperature and generated a combustible air mixture in the vapor layer of the tank.
2. When the solvent was loaded from another tank to a tank lorry, the blower was turned on to feed it to the deodorization tower. The vapor from the vapor layer of the tank entered the deodorization piping. The vapor piping for deodorization was shared among multiple tanks including the tank concerned.
3. At the end of the deodorization piping, an expansion work was carried out using fire.
4. Fire in the piping was ignited by welding sparks, and spread to the tank. |
| Countermeasures |
The basics of safety management should be observed. |
| Knowledge Comment |
1. Indifference to safety and the inadequate management system (chain of command) are the main reasons for accidents.
2. As accidents causing offensive smell or stimulative materials have big impacts on neighboring inhabitants, special consideration should be given to safety management. |
| Background |
1. Hot work was carried out without separating or purging the piping (deodorization piping) from the tank with dangerous materials. Safety was neglected.
2. Storage of solvents was started in the tank without waiting for the completion of the facilities for safety. The cooling system should have prevented the generation of a flammable gas-air mixture.
3. No attention was paid to the vapor piping connecting the tank and the deodorizer. Although the temperature was measured in the tank, anyone did not care about the generation of a combustible gas-air mixture. The cause was nothing but mismanagement. |
| Reason for Adding to DB |
Example of accident occurred due to a lack of awareness about fire properties of materials |
| Scenario |
| Primary Scenario
|
Poor Value Perception, Poor Safety Awareness, Inadequate Risk Recognition, Organizational Problems, Poor Management, Inadequate Operation Management, Ignorance, Insufficient Knowledge, Insufficient Study, Usage, Operation/Use, Operation of Uncomplted Equipment, Malicious Act, Rule Violation, Safety Rule Violation, Bad Event, Chemical Phenomenon, Vaporization/Leakage, Secondary Damage, External Damage, Fire, Bodily Harm, Injury, 2 person injured, Loss to Organization, Economic Loss, Direct Monetary Damage 90 million yen
|
|
| Sources |
High Pressure Gas Safety Inst. of Japan. High pressure gas protection overview. pp.218-219, 222(1990).
Fire and Disaster Management Agency. Major cases of accidents. Explosion and fire at an outdoor tank. Accident cases of dangerous materials. pp.32, 98-99
|
| Number of Injuries |
2 |
| Physical Damage |
The tank roof blew off and the upper part of the tank was deformed by heat. Ethyl acrylate burned. |
| Financial Cost |
¥ 94 million. (Accident cases of dangerous materials) |
| Consequences |
A wide diffusion of offensive smell of ethyl acrylate that remained without burning. |
| Multimedia Files |
Fig3.Chemical formula
|
| Field |
Chemicals and Plants
|
| Author |
WAKAKURA, Masahide (Kanagawa Industrial Technology Research Institute)
TAMURA, Masamitsu (Center for Risk Management and Safety Sciences, Yokohama National University)
|