| Case Name |
Explosion of dinitrosopentamethylenetetramine(DPT) during continuous operation of the rotary valve for measuring DPT caused due to frictional heat because of continuously abnormal condition |
| Pictograph |
|
| Date |
May 19, 1972 |
| Place |
Himeji, Hyogo, Japan |
| Location |
Chemical factory |
| Overview |
Explosion occurred in the drying section of a dinitrosopentamethylenetetramine (DPT) manufacturing plant. The flames went up into the upper part of the hopper when dried manufactured goods were stored in the hopper and weighed, and the bag filter exploded. It was supposed that fine DPT powder was ignited by frictional heat from the rotary valve being adjusted from the previous day, and that it ignited the DPT in the product hopper. |
| Incident |
In a drying section of a dinitrosopentamethylenetetramine (DPT) manufacturing plant, the manufactured goods are dried and stored in a measuring hopper, and are weighed. Flames were generated in the upper manhole of the measuring hopper while weighing. The bag filter at the inlet side of the measuring hopper exploded, and the drying section was destroyed. |
| Processing |
Manufacture |
| Individual Process |
Transfer |
| Substance |
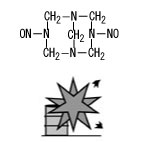
N,N'-dinitrosopentamethylenetetramine(DPT), Fig2 |
| Type of Accident |
Fire, explosion |
| Sequence |
On May 18th, 1972: A grating sound was heard from the rotary valve mounted in vertical piping between a bug filter and a measuring hopper.
On May 19th: The rotary valve had been adjusted while operating the DPT plant. The manufacturing goods were stored after drying in the hopper for measurement as usual. The flames were generated near the manhole of the upper hopper, and the bag filter exploded. |
| Cause |
A possible scenario of the explosion was as follows. The rotary valve had been adjusted due to a grating sound heard on the day before the accident. Dry DPT was ignited by frictional heat from the operating rotary valve. Burning DPT was sent further into the hopper. DPT that remained in the hopper exploded. |
| Countermeasures |
Manufacturing work is stopped while maintenance of equipment and facilities is being carried out. |
| Knowledge Comment |
It is necessary to study carefully whether to discontinue manufacturing or to continue when checking and repair work of a plant are executed. In addition, operation should be stopped if there is even a small concern. When energetic materials or a light hydrocarbons are handled, such consideration is especially necessary. |
| Background |
It seems that the grating sound of the rotary valve was caused by unnecessary friction. If a combustible fine particle passes over a part where there is friction, it is assumed naturally that it will be ignited by frictional heat. The problem was that DPT continued to be supplied through the rotary valve without thinking about this fact. It is necessary to take account of friction, considering the properties of the substance being handled. It is considered that safety management was lacking in the operation. |
| Reason for Adding to DB |
Example of accident caused due to a repair work done during usual preparation operation |
| Scenario |
| Primary Scenario
|
Organizational Problems, Poor Management, Slackness of Management, Poor Value Perception, Poor Safety Awareness, Inadequate Risk Recognition, Misjudgment, Misjudgment of Situation, Malicious Act, Rule Violation, Safety Rule Violation, Usage, Operation/Use, Operation of Machine, Bad Event, Mechanical Event, Friction, Bad Event, Chemical Phenomenon, Heat Generation/Ignition, Secondary Damage, External Damage, Explosion
|
|
| Sources |
Japan Assoc. of Fire Science and Engineering, Chemistry fire committee, A.7.2, Organic blowing agent, Case 186, Chemistry fire examples (2), p.21(1974).
Masamitsu Tamura, Masahide Wakakura, Dinitrosopentamethylenetetramine explosion, Reaction danger -Accident case and analysis - p.142(1995).
|
| Physical Damage |
Destruction of the drying section |
| Multimedia Files |
Fig2.Chemical formula
|
| Field |
Chemicals and Plants
|
| Author |
OGAWA, Terushige (Graduate School of Environment and Information Sciences, Yokohama National University)
TAMURA, Masamitsu (Center for Risk Management and Safety Sciences, Yokohama National University)
|
|