| Case Name |
Explosion of an organic peroxide catalyst during circulation before use at a crosslinked polyethylene manufacturing plant |
| Pictograph |
|
| Date |
November 18, 1990 |
| Place |
Kawasaki, Kanagawa, Japan |
| Location |
Chemical factory |
| Overview |
On November 18th, 1990, an explosion occurred in catalyst (organic peroxide) supply facilities at a polyethylene manufacturing plant. It might have been caused due to foreign matter contamination. |
| Incident |
The change of a catalyst for crosslinking for the brand changing at a plant manufacturing crosslinked polyethylene from polyethylene. Two hours after the circulation of 2, 5-dimethyl-2, 5-di-t-butylperoxyhexyne-3(Perhexyne25B) between the dissolving drum and pump started, an explosion and a fire occurred. |
| Processing |
Manufacture |
| Individual Process |
Reaction |
| Process Flow |
Fig2.Process flow sheet
|
|
Fig3.Progress Flow
|
| Chemical Reaction |
Polymerization |
| Substance |
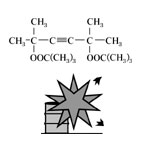
2,5-dimethyl-2,5-di-t-butylperoxyhexyne-3(2,5-dimethyl-2,5-di-t-butylperoxyhexyne-3), Fig4 |
| Type of Accident |
Explosion, fire |
| Sequence |
Substitution of Perhexyne25B for used organic peroxide started on November 16th, 1990, two days before the fire. First, hot water at 50 °C was passed through the jackets in the system for heating and peroxide used last time was dissolved. After that, it was collected from all drain valves and substituted with Perhexyne25B. Completion of substitution was judged by the color of solution dripping from drains.
At 9:00, 18th; Perhexyne25B was poured into the dissolving tank.
About 12:30; the pump started working and the circulation operation started.
About 14:30; an explosion occurred and fire broke out at the same time in the second dissolution operation room. |
| Cause |
Perhexyne25B was decomposed in the second filter due to foreign matter contamination. A filter was destroyed by decomposed gas. A fire and an explosion occurred due to spontaneous combustion or static electricity. |
| Response |
Emergency shutdown |
| Countermeasures |
Perhexyne supply piping and other peroxide supply lines should be separated.
Reinforcement of operation observation such as monitoring temperature and a flow rate and an automatic shutdown system and so on should be executed.
The cooling water supply-line for an unusual reaction should be installed. |
| Knowledge Comment |
In handling substances that can easily decompose or explode such as organic peroxide, it is necessary to take great care to their concentration, temperature and contamination with foreign materials. |
| Background |
The cause has not been specified.
Strengthening of operation management should be considered. |
| Reason for Adding to DB |
Example of explosion accident of organic peroxide |
| Scenario |
| Primary Scenario
|
Insufficient Analysis or Research, Insufficient Practice, Lack of Imagination, Organizational Problems, Poor Management, Slackness of Management, Carelessness, Insufficient Precaution, Inadequate Handling, Planning and Design, Poor Planning, Poor Design, Bad Event, Chemical Phenomenon, Abnormal Reaction, Secondary Damage, External Damage, Explosion/Fire, Bodily Harm, Injury, 1 person injured, Loss to Organization, Economic Loss, Direct Manetary Damage 20 million yen
|
|
| Sources |
M. Tamura, M. Wakakura, "Explosion of 2,5-dimethyl-2,5-di-t-butylperoxyhexyne-3", Reaction danger.- Accident case and analysis - p.159(1995)
Society for the study of hazardous substances of Kawasaki City, Cases of accident cases with dangerous materials. (with FTA), pp.50-52(1997)
Hazardous Materials Safety Techniques Association, Cases of accidents with hazardous materials seminar, pp.76-77(1996)
Kawasaki city Fire fighting station, Prevention division, Peace section. Outline of accident of fire and explosion at NU Co. special polyethylene manufacturing plant. Material of the Kawasaki city complex safety countermeasure committee.
|
| Number of Injuries |
1 |
| Physical Damage |
Damage to approx. 66 square meters of a steel slated five-story building, Perhexyne burned. Damage to pumps, filters, two drums and attached facilities and approx. 30 square meters of the external wall of the storage for carbon. 250 kg of carbon in two bags partially burned.(Kawasaki City fire department) |
| Financial Cost |
¥ 21 million (material of the Kawasaki City complex safety countermeasures committee) |
| Multimedia Files |
Fig4.Chemical formula
|
| Notes |
Self-heating decomposition |
| Field |
Chemicals and Plants
|
| Author |
WADA, Yuji (National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology)
TAMURA, Masamitsu (Center for Risk Management and Safety Sciences, Yokohama National University)
|
|