| Case Name |
Ignition of leaked gas caused due to a runaway reaction during a power failure at an expanded polystyrene manufacturing plant |
| Pictograph |
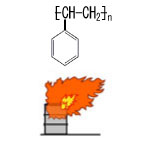
|
| Date |
October 11, 1995 |
| Place |
Kamisu, Ibaragi, Japan |
| Location |
Chemical factory |
| Overview |
A fire occurred at an expanded polystyrene plant. Cooling water and an agitator of the polymerization reactor stopped due to a power failure. A polymerization inhibitor could not be supplied, and there was a runaway reaction. Styrene polymerization material discharged from a relief valve for pressure discharge was ignited. Surroundings were damaged by fire. The problem lay in safety management, such as management of insulation oil of a disconnecting switch, and maintenance management of an emergency pump. |
| Incident |
A fire occurred at an expanded polystyrene manufacturing plant. Cooling water and an agitator of a polymerization reactor were stopped by a power failure. The reaction ran away and pressure rose. A polymerization inhibitor was not able to be supplied. Gas was discharged through a vent piping into the atmosphere. The discharged gas ignited, and an electric cable nearby burned. It was assumed that the source of ignition was static electricity. |
| Processing |
Manufacture |
| Individual Process |
Reaction |
| Process Flow |
Fig2.Unit process flow
|
| Chemical Reaction |
Polymerization |
| Chemical Equation |
Fig3.Chemical reaction formula
|
| Substance |
Polystyrene, Fig4 |
| Styrene, Fig5 |
| Type of Accident |
Fire |
| Sequence |
08:12 on October 11th, 1995. The electricity of a part of the factory was cut off. Cooling water and an agitator stopped at a polymerization reactor. The pressure of the reactor under a polymerization reaction rose.
08:23. As an injection pump of a polymerization inhibitor could not be driven, injection of the polymerization inhibitor failed. Although a liquid blow down valve was opened, the contents did not flow out immediately due to their viscosity.
Pressure rose to 0.17 MPaG.
08:35. To prevent a rupture of the reactor, a relief valve was opened.
08:40. Styrene polymer blown from the relief valve ignited. Nearby electric cables burned.
08:42. The public fire department was notified of the fire. Five fire engines and 26 fire fighters turned out.
09:15. The fire was confirmed to have been extinguished. |
| Cause |
The cause of the power failure was a short circuit with the ground due to degradation of insulation oil of a disconnecting switch of a main power supply line. Moreover, the cause of the operation failure of the pump for polymerization inhibitor injection was inadequate maintenance. The cause of ignition was static electricity on a discharge to the atmosphere. |
| Response |
Due to the power failure, an outdoor fire hydrant and indoor bubble firefighting equipment did not operate. The office personnel extinguished the fire with 22 fire extinguishers.
A water tap etc. could not be used although five chemical fire engines and 26 persons turned out.
The fire was extinguished by spraying water from one tank car. |
| Countermeasures |
Duplicating power supply system for a firefighting water pump.
A new firefighting water pump is installed which can be operated with both an engine and an electrical motor.
A new electric generator only for a security power source is established.
A tank is installed for a polymerization inhibitor and nitrogen pressurizing is conducted.
A buffer tank is installed in relief piping.
Insulating diagnosis is added to check items of electric equipment. |
| Knowledge Comment |
Even if a security power supply generator for emergency is installed, the power supply will fail if the supply system breaks down when there is only one power supply system. Failure of power supply facilities, such as a substation, also brings the same result.
Dual systems and decentralization are indispensable for a power system such as electricity, air, and oil pressure.
Fire extinguishing methods not using fire fighting equipment have to be assumed. |
| Background |
It seems that consciousness of safety design and safety management was insufficient. Insulation oil deteriorates with long-term use, so it should be checked periodically. Injection equipment of the polymerization inhibitor for an emergency should be maintained so that it could work at any time. If possible, not a pump but a more reliable method should be adopted. If possible, discharged gas in an emergency should be processed by combustion. If this is not possible, it should be discharged to a safe place, for example, a high point. |
| Reason for Adding to DB |
Example of fire caused due to some inadequate safety management |
| Scenario |
| Primary Scenario
|
Organizational Problems, Poor Management, Slackness of Management, Poor Value Perception, Poor Safety Awareness, Insufficient Safety Measure, Carelessness, Insufficient Understanding, Insufficient Recognition of Risk, Planning and Design, Poor Planning, Poor Design, Bad Event, Electrical Failure, Power Failure, Bad Event, Chemical Phenomenon, Abnormal Reaction, Secondary Damage, External Damage, Leakage/Fire, Loss to Organization, Economic Loss, Manetary Damage 80 million yen
|
|
| Sources |
Fire and Disaster Management Agency, Expanded polystyrene resin manufacturing plant fire, Accident cases of dangerous materials. 1995, pp.222-223.
The Kashima south district fire-fighting office work union. Fire-Defense Headquarters. Tamotsu Tsukamoto. Expanded polystyrene resin manufacturing plant fire accident. Dangerous object accident case seminar, pp.15-23(1997).
|
| Physical Damage |
A polymerization reactor and related piping, outer walls, a cable rack, and wiring of a polymerization building were damaged. |
| Financial Cost |
¥ 80 million (Fire and Disaster Management Agency).
¥ 37 million (The southern KAJIMA area fire fighting headquarters). |
| Multimedia Files |
Fig4.Chemical formula
|
|
Fig5.Chemical formula
|
| Field |
Chemicals and Plants
|
| Author |
ITAGAKI, Haruhiko (Japan National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health)
TAMURA, Masamitsu (Center for Risk Management and Safety Sciences, Yokohama National University)
|
|