| Case Name |
Fire caused due to a thunderbolt that struck piping at a vinyl chloride monomer manufacturing plant |
| Pictograph |
|
| Date |
September 11, 1987 |
| Place |
Kawasaki, Kanagawa, Japan |
| Location |
Chemical Factory |
| Overview |
The pump discharge piping of the plant manufacturing a vinyl chloride monomer from ethane dichloride was damaged when a thunderbolt struck and caused a fire. There was piping corrosion caused by aging deterioration as well as partial reduction of thickness due to erosion from turbulence caused by closing of the valve. The impact of the thunderbolt triggered off the rupture of piping. Insufficient maintenance resulted in aging deterioration. Periodic maintenance is necessary. |
| Incident |
The plant, which manufactures vinyl chloride monomers and hydrogen chloride from ethane dichloride, was under usual operation. Vinyl chloride monomers and hydrogen chloride spouted from the discharge piping of the circulation pump of the quenching tower located at the outlet of the ethane dichloride cracker, and caused a fire. |
| Processing |
Manufacture |
| Individual Process |
Reaction |
| Chemical Reaction |
Other (Cracking) |
| Substance |
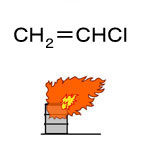
Vinyl chloride, Fig2 |
| Type of Accident |
Leakage, fire |
| Sequence |
On the eleventh day after restarting operation after turnaround shutdown maintenance, there was heavy rain in the afternoon. No sooner had a thunderbolt struck, than the alarm of the quenching tower sounded to inform operators of an abnormal flow. A fire occurred almost simultaneously, and the whole plant was engulfed in flames after two explosions. |
| Cause |
Part of the discharge piping of the circulation pump was markedly thin due to corrosion caused by aging deterioration and erosion when the circulation pump outlet valve was closed to control the flow. The thunderbolt that struck the neighboring area shook equipment and piping severely. Combined with operation pressure, this vibration damaged the corrosive part of the piping. |
| Response |
Emergency shutdown of the plant. |
| Countermeasures |
Establishment of countermeasures against a thunderbolt and establishment of the proper facilities management system to ensure that piping will not be ruptured by a thunderbolt. |
| Knowledge Comment |
On handling hazardous materials, it is necessary to identify the points with a risk of leakage and establish safety measures on the assumption of the worst-case scenario. |
| Background |
The maintenance was not sufficient, although the piping was used for corrosive liquids. The type of valve, which controlled the flow, was not clear from the description in the report, which says that it was a sluice valve. However, it seems to have produced a large turbulent flow, which caused erosion. Turbulent flows of corrosive liquids accelerate corrosion. Similar cases are seen in other processes. The question remains if the materials were selected properly where the turbulent flow existed and if the flow was controlled properly. |
| Reason for Adding to DB |
Example of accident showing the importance of plant maintenance |
| Scenario |
| Primary Scenario
|
Poor Value Perception, Poor Safety Awareness, Inadequate Risk Recognition, Carelessness, Insufficient Understanding, Insufficient Recognition of Risk, Usage, Maintenance/Repair, Insufficient Inspection, Planning and Design, Poor Planning, Poor Design, Bad Event, Thermo-Fluid Event, Erosion by Turbulant Flow, Failure, Abrasion, Corrosion, Secondary Damage, External Damage, Explosion/Fire, Loss to Organization, Economic Loss, Direct Monetary Damage 14 million yen
|
|
| Sources |
High Pressure Gas Safety Inst. of Japan, Accident related to Vinyl chloride. High pressure gas protection overview, p.113(1988).
High Pressure Gas Safety Inst. of Japan. List of accident related to High Pressure Gas Control Law in 1987. High-pressure gas protection overview. pp.104-105(1988).
Kawasaki city Fire fighting station Prevention division, Peace section. Outline of fire at C chemical Co,Ltd. VCM manufacturing plant. Material of the Kawasaki City Complex safety countermeasure committee
|
| Physical Damage |
Two quenching towers, their circulation pumps and other equipment and piping, and electrical wiring were damaged by fire. About seven tons of chemical substances including a vinyl chloride monomer and ethane dichloride burned. |
| Financial Cost |
¥ 1.4 million. (Material of the Kawasaki City Complex safety countermeasure committee) |
| Multimedia Files |
Fig2.Chemical formula
|
| Field |
Chemicals and Plants
|
| Author |
WAKAKURA, Masahide (Kanagawa Industrial Technology Research Institute)
TAMURA, Masamitsu (Center for Risk Management and Safety Sciences, Yokohama National University)
|
|